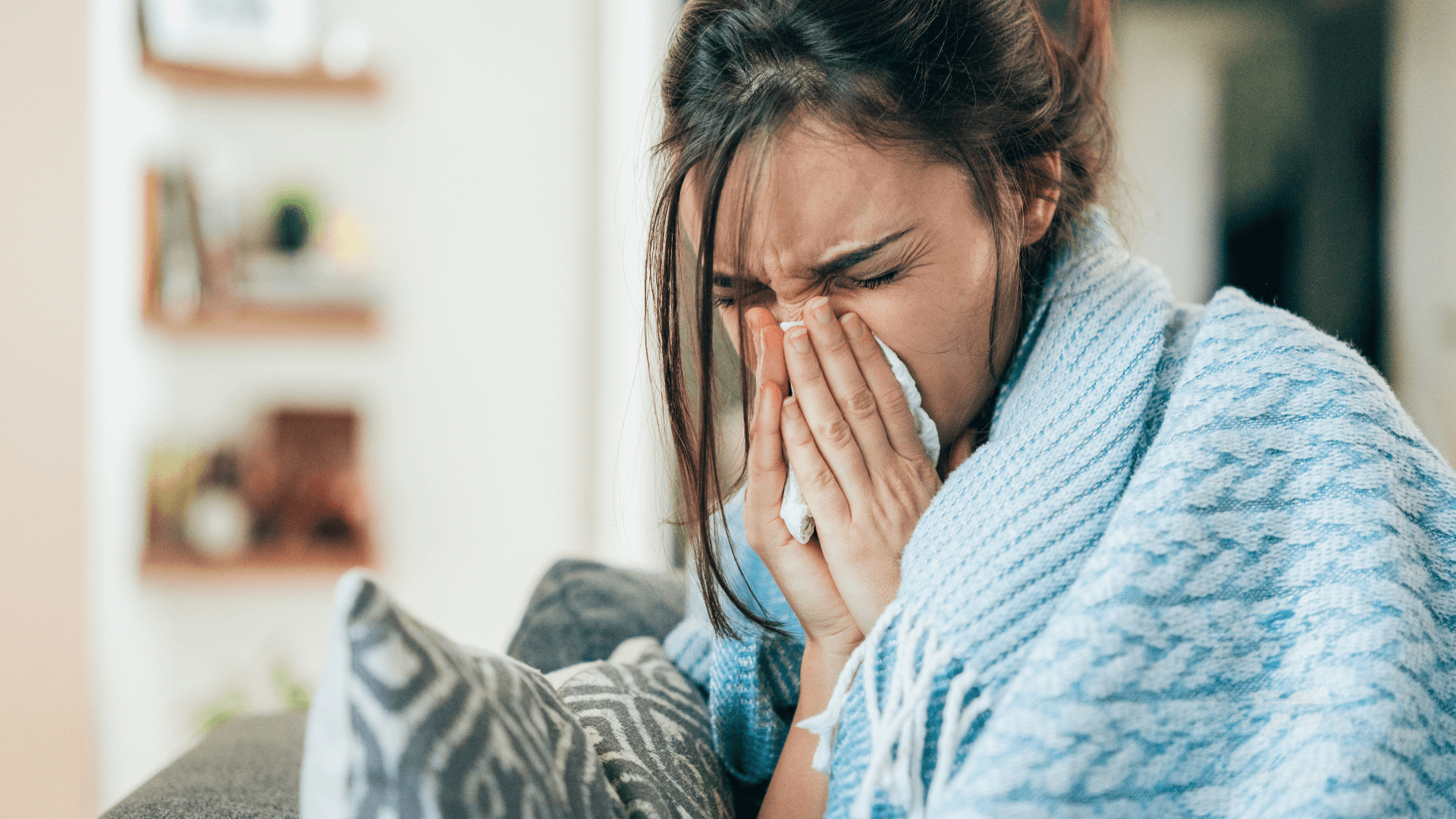

Common cold: recognition, symptoms and management
Colds are microbial infections of the upper respiratory tract caused by various viruses.
Colds last an average of one week, but can be prolonged, especially in children, the elderly and people with compromised immune systems. Adults get an average of two to four colds per year, mostly between September and May. Young children may have six to eight colds a year.
Cold symptoms
Cold symptoms usually appear within 1 to 3 days after a virus enters the body. The main symptoms include:
Runny nose
Buboes
Sneezing
Weakened sense of taste and smell
Sore throat
Coughing
Children and infants are more likely to develop a fever compared to adults and adolescents. In smokers, symptoms may be more severe than in non-smokers.
Cold prevention
Colds are highly contagious and are mainly transmitted through the air or direct contact. To prevent colds:
Avoid close contact with people who have a cold.
Wash your hands often with soap and water.
Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth with your hands.
Treating colds
Over-the-counter medicines can provide temporary relief from cold symptoms. Decongestants and antihistamines can help relieve nasal discharge and coughing. It is important to follow dosage instructions and avoid overuse of medications. Antibiotics are not effective for treating colds because colds are caused by viruses, not bacteria. If you experience severe symptoms or if symptoms do not improve over time, contact your doctor.
 El. Venizelou 220, Limenas Hersonissos 700 14
El. Venizelou 220, Limenas Hersonissos 700 14 (+30) 2897 302 900
(+30) 2897 302 900 info@primehealthmed.gr
info@primehealthmed.gr