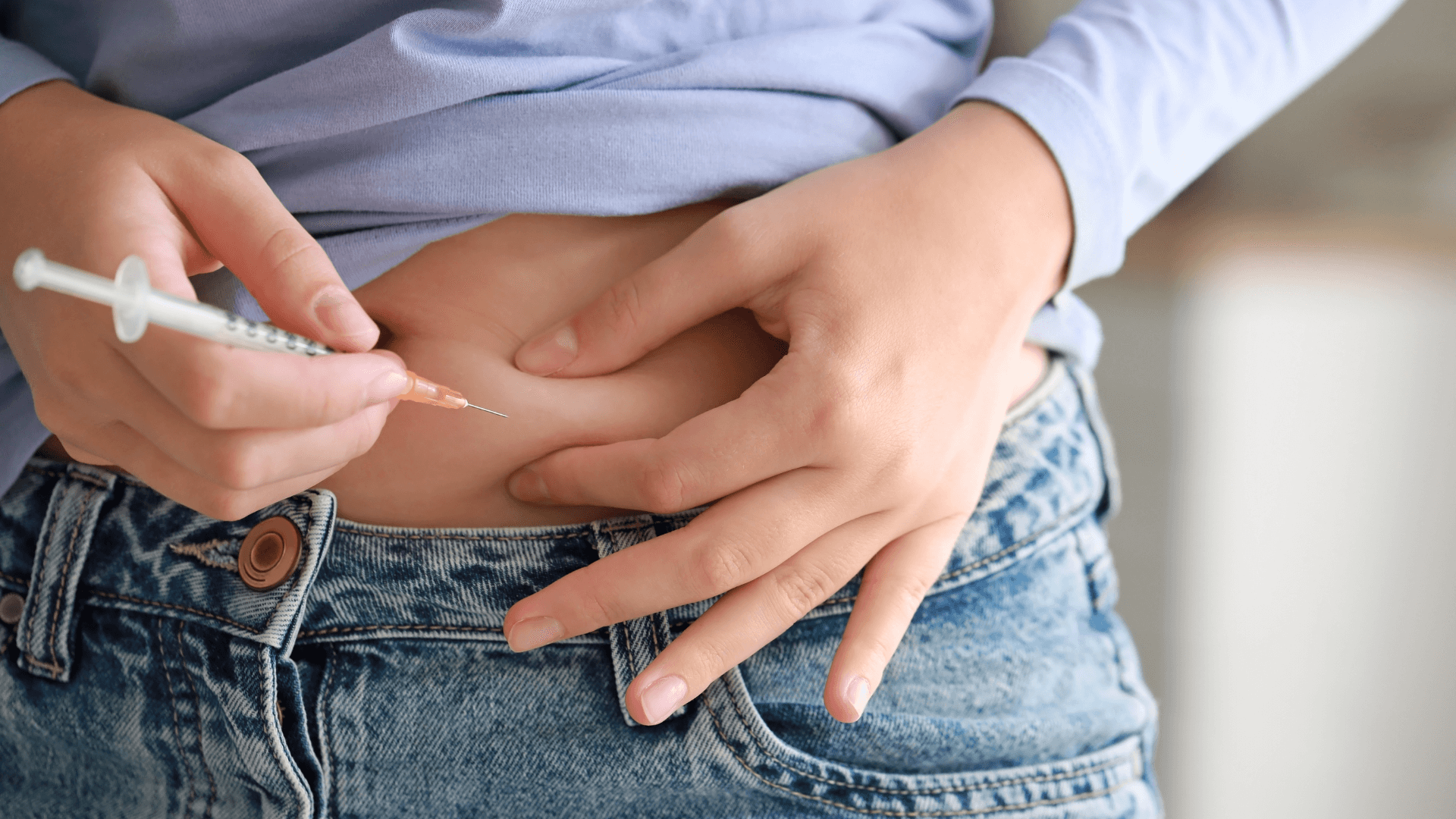

What is diabetes mellitus in children?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects the way the body handles glucose, the predominant energy fuel from the diet.
In diabetes mellitus, the body's production or sensitivity to the hormone insulin is disrupted, leading to excessively high blood glucose levels.
There are two main types of diabetes mellitus that can affect children:
Type 1: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Patients with type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily to manage blood glucose levels.
Type 2: Type 2 diabetes is most common in adults, but can also occur in children. In this case, the body does not produce enough insulin or does not properly utilize the insulin that is produced. Usually the management of Type 2 diabetes involves diet, exercise and in some cases medical treatment.
In children with diabetes mellitus, there are some common symptoms that parents should monitor. These are:
Increased sense of thirst
Frequent urination, especially at night
Increased hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Changes in behaviour
Bad breath smell
If your child is experiencing these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for evaluation and diagnosis. Managing diabetes mellitus in children requires careful monitoring, frequent check-ups and working with specialists to ensure a healthy life.
 El. Venizelou 220, Limenas Hersonissos 700 14
El. Venizelou 220, Limenas Hersonissos 700 14 (+30) 2897 302 900
(+30) 2897 302 900 info@primehealthmed.gr
info@primehealthmed.gr